Resumen
Resumen
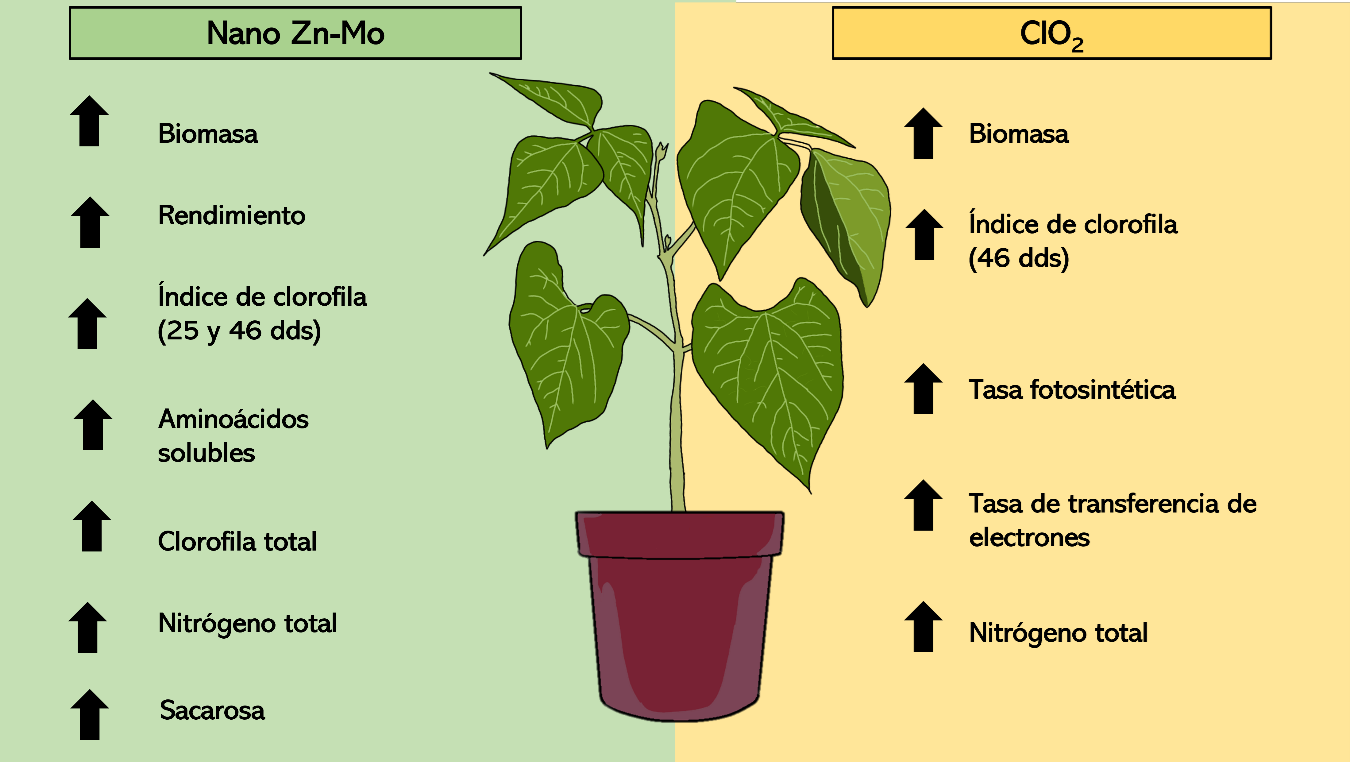
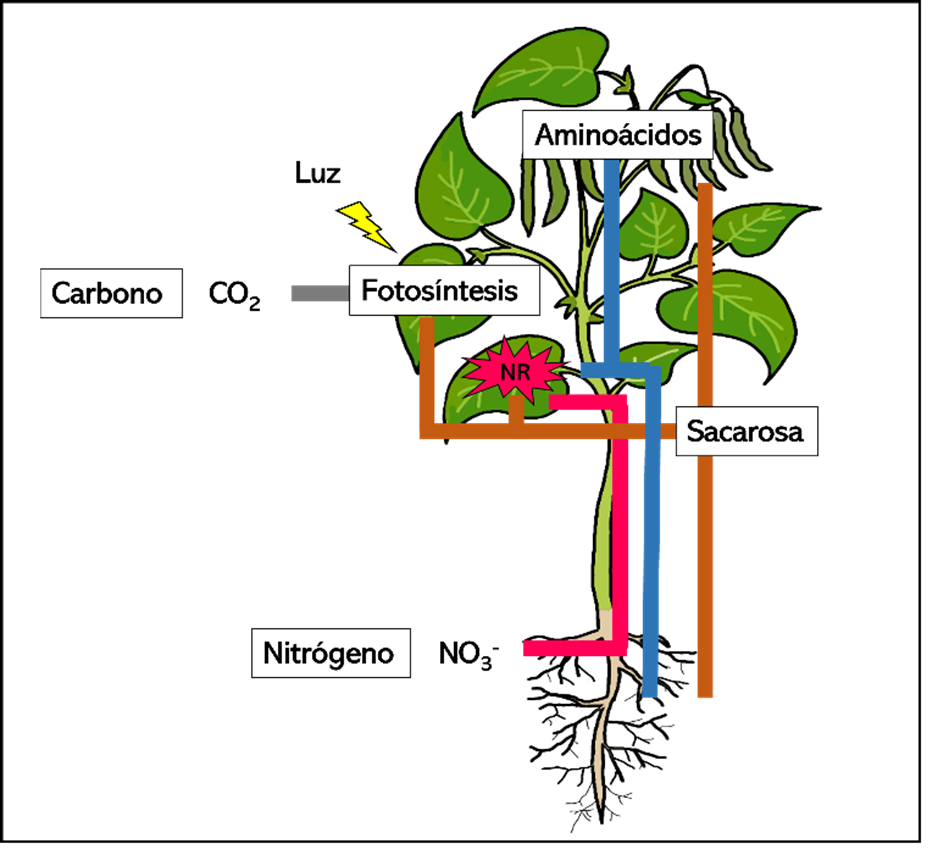
La producción de alimentos de forma sustentable es un reto para la agricultura moderna. Una alternativa para incrementar el rendimiento de los cultivos es la utilización de fertilizantes que permitan una reducción de insumos como los nanofertilizantes y aspersiones foliares con nutrientes en forma de gas. Combinaciones de nano Zn y Mo, así como el dióxido de cloro (ClO2), han mostrado resultados favorables. Sin embargo, la información acerca del uso de nanofertilizantes de Zn y Mo y ClO2 y su efecto en el metabolismo primario y rendimiento en plantas de frijol es escasa. Por lo tanto, el objetivo del presente estudio fue determinar el efecto de la aplicación foliar de nano Zn-Mo y ClO2 sobre la asimilación de nitrógeno, carbono y su relación con el rendimiento de plantas de frijol. Plantas de frijol ejotero (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) cv Strike se desarrollaron durante 53 días. Se compararon la aplicación de ClO2 a 30 ppm, nano Zn-Mo a 4 ppm y un control sin aplicación. La aplicación de nano Zn-Mo incrementó biomasa, rendimiento, índice de clorofila, aminoácidos solubles, clorofila total y sacarosa. La aplicación de ClO2, favoreció la biomasa, la tasa fotosintética y la tasa de transporte de electrones. Finalmente, los resultados sugieren que la asimilación de carbono está integrada a la asimilación de nitrógeno y que la aplicación foliar de nano Zn-Mo podría tener la capacidad de impulsar ambos metabolismos y mejorar el rendimiento en plantas de frijol ejotero.
Citas
Al-Mamun, M. R., Hasan, M. R., Ahommed, M. S., Bacchu M. S., Ali, M. R., & Khan, M. Z. H. (2021). Nanofertilizers towards sustainable agriculture and environment. Environmental Technology & Innovation, 23, 101658.https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eti.2021.101658
Alexander, P., Rounsevell, M. D., Dislich, C., Dodson, J. R., Engström, K., & Moran, D. (2015). Drivers for global agricultural land use change: The nexus of diet, population, yield and bioenergy. Global Environmental Change, 35, 138-147.https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gloenvcha.2015.08.011
Ben Amor, N., Megdiche, W., Jiménez, A., Sevilla, F., & Abdelly, C. (2010). The effect of calcium on the antioxidant systems in the halophyte Cakile maritima under salt stress. Acta Physiologiae Plantarum, 32, 453-461.https://doi.org/10.1007/s11738-009-0420-2
Bharti, K., Pandey, N., Shankhdhar, D., Srivastava, P. C., & Shankhdhar, S. C. (2014). Effect of exogenous zinc supply on photosynthetic rate, chlorophyll content and some growth parameters in different wheat genotypes. Cereal Research Communications, 42, 589-600.https://doi.org/10.1556/CRC.2014.0015
Bloom, A. J. (2015). Photorespiration and nitrate assimilation: a major intersection between plant carbon and nitrogen. Photosynthesis research, 123(2), 117-128.https://doi.org/10.1007/s11120-014-0056-y
Chen, J., Yin, Y., Zhu, Y., Song, K., & Ding, W. (2023). Favorable physiological and morphological effects of molybdenum nanoparticles on tobacco (Nicotiana tabacum L.): root irrigation is superior to foliar spraying. Frontiers in Plant Science, 14, 1220109 https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2023.1220109
Cunha, A. R. D., Katz, I., Sousa, A. D. P., & Martinez Uribe, R. A. (2015). Índice SPAD en el crecimiento y desarrollo de plantas de lisianthus en función de diferentes dosis de nitrógeno en ambiente protegido. Idesia (Arica), 33(2), 97-105.http://dx.doi.org/10.4067/S0718-34292015000200012
Du, W., Yang, J., Peng, Q., Liang, X., & Mao, H. (2019). Comparison study of zinc nanoparticles and zinc sulphate on wheat growth: From toxicity and zinc biofortification. Chemosphere, 227, 109-116.https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.03.168
Franco-Navarro, J. D., Brumós, J., Rosales, M. A., Cubero-Font, P., Talón, M., & Colmenero-Flores, J. M. (2016). Chloride regulates leaf cell size and water relations in tobacco plants. Journal of Experimental Botany, 67(3), 873-891.https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/erv502
Ghasemi, S., Khoshgoftarmanesh, A. H., Afyuni, M., & Hadadzadeh, H. (2013). The effectiveness of foliar applications of synthesized zinc-amino acid chelates in comparison with zinc sulfate to increase yield and grain nutritional quality of wheat. European Journal of Agronomy, 45, 68-74.https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eja.2012.10.012
Geilfus, C. M. (2018). Review on the significance of chlorine for crop yield and quality. Plant Science, 270, 114-122.https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plantsci.2018.02.014
Govindan, K. (2018). Sustainable consumption and production in the food supply chain: A conceptual framework. International Journal of Production Economics, 195, 419-431.https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpe.2017.03.003
Gutiérrez-Ruelas, N. J., Palacio-Márquez, A., Sanchez, E., Muñoz-Márquez, E., Chávez-Mendoza, C., Ojeda-Barrios, D. L., & Flores-Cordova, M. A. (2021). Impact of the foliar application of nanoparticles, sulfate and iron chelate on the growth, yield and nitrogen assimilation in green beans. Notulae Botanicae Horti Agrobotanici Cluj-Napoca, 49(3), 12437-12437.https://doi.org/10.15835/nbha49312437
Herdean, A., Teardo, E., Nilsson, A. K., Pfeil, B. E., Johansson, O. N., Ünnep, R., Nagy, G., Zsiros, O., Dana, S., Solymosi, K., Garab, G., Szabó, I., Cornelia Spetea & Lundin, B. (2016). A voltage-dependent chloride channel fine-tunes photosynthesis in plants. Nature communications, 7(1), 11654.https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms11654
Hildebrandt, T. M., Nesi, A. N., Araújo, W. L., & Braun, H. P. (2015). Amino acid catabolism in plants. Molecular plant, 8(11), 1563-1579.https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molp.2015.09.005
Imran, M., Sun, X., Hussain, S., Ali, U., Rana, M. S., Rasul, F., Saleem, M. H., Mohamed, G. M., Parashuram, B., Javaria, A., Ali, M. E. & Hu, C. X. (2019). Molybdenum-induced effects on nitrogen metabolism enzymes and elemental profile of winter wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) under different nitrogen sources. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 20(12), 3009.https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20123009
Irigoyen, J. J., Einerich, D. W., & Sánchez‐Díaz, M. (1992). Water stress induced changes in concentrations of proline and total soluble sugars in nodulated alfalfa (Medicago sativa) plants. Physiologia plantarum, 84(1), 55-60.https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1399-3054.1992.tb08764.x
Kaiser, B. N., Gridley, K. L., Ngaire Brady, J., Phillips, T., & Tyerman, S. D. (2005). The role of molybdenum in agricultural plant production. Annals of Botany, 96(5), 745-754.https://doi.org/10.1093/aob/mci226
Khan, N., Tariq, M., Ullah, K., Muhammad, D., Khan, I., Rahatullah, K., & Ahmed, S. (2014). The effect of molybdenum and iron on nodulation, nitrogen fixation and yield of chickpea genotypes (Cicer arietinum L.). IOSR Journal of Agriculture and Veterinary Science, 7(1), 63-79.https://www.iosrjournals.org/iosr-javs/papers/vol7-issue1/Version-3/L07136379.pdf
Lawlor, D. W. (2002). Carbon and nitrogen assimilation in relation to yield: mechanisms are the key to understanding production systems. Journal of experimental Botany, 53(370), 773-787.https://doi.org/10.1093/jexbot/53.370.773
Leghari, S. J., Wahocho, N. A., Laghari, G. M., HafeezLaghari, A., MustafaBhabhan, G., HussainTalpur, K., & Lashari, A. A. (2016). Role of nitrogen for plant growth and development: A review. Advances in Environmental Biology, 10(9), 209-219. https://go.gale.com/ps/anonymous?id=GALE%7CA472372583&sid=googleScholar&v=2.1&it=r&linkaccess=abs%0D
Liu, L., Xiao, W., Li, L., Li, D. M., Gao, D. S., Zhu, C. Y., & Fu, X. L. (2017). Effect of exogenously applied molybdenum on its absorption and nitrate metabolism in strawberry seedlings. Plant Physiology and Biochemistry, 115, 200-211. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plaphy.2017.03.015
Liu, C., Hu, C., Tan, Q., Sun, X., Wu, S., & Zhao, X. (2019). Co-application of molybdenum and zinc increases grain yield and photosynthetic efficiency of wheat leaves. Plant, Soil and Environment, 65(10), 508-515. https://doi.org/10.17221/508/2019-PSE
Mahdieh, M., Sangi, M. R., Bamdad, F., & Ghanem, A. (2018). Effect of seed and foliar application of nano-zinc oxide, zinc chelate, and zinc sulphate rates on yield and growth of pinto bean (Phaseolus vulgaris) cultivars. Journal of Plant Nutrition, 41(18), 2401-2412. https://doi.org/10.1080/01904167.2018.1510517
Tejada-Jimenez, M., Chamizo-Ampudio, A., Llamas, A., Galván, A., & Fernandez, E. (2018). Roles of molybdenum in plants and improvement of its acquisition and use efficiency. In Plant micronutrient use efficiency (pp. 137-159). Academic Press. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-812104-7.00009-5
Monreal, C. M., DeRosa, M., Mallubhotla, S. C., Bindraban, P. S. & Dimkpa, C. 2016. Nanotechnologies for increasing the crop use efficiency of fertilizer-micronutrients. Biology and fertility of soils, 52, 423-437. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00374-015-1073-5
Muñoz-Márquez, E., Soto-Parra, J. M., Noperi-Mosqueda, L. C., & Sánchez, E. (2022a). Application of molybdenum nanofertilizer on the nitrogen use efficiency, growth and yield in green beans. Agronomy, 12(12), 3163. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12123163
Muñoz-Márquez, E., Soto-Parra, J. M., Pérez-Leal, R., Yánez-Muñoz, R. M., Noperi-Mosqueda, L. C., & Sánchez-Chávez, E. (2022b). Aplicación de nanomolibdeno en frijol y su impacto sobre la eficiencia del nitrógeno. Revista Mexicana de Ciencias Agrícolas, 13(SPE28), 319-329. https://doi.org/10.29312/remexca.v13i28.3286
Qaim, M. (2020). Role of new plant breeding technologies for food security and sustainable agricultural development. Applied Economic Perspectives and Policy, 42(2), 129-150. https://doi.org/10.1002/aepp.13044
Pardey, P. G., Beddow, J. M., Hurley, T. M., Beatty, T. K., & Eidman, V. R. (2014). A bounds analysis of world food futures: Global agriculture through to 2050. Australian Journal of Agricultural and Resource Economics, 58(4), 571-589. https://doi.org/10.1111/1467-8489.12072
Pokhrel, R., McConnell, I. L., & Brudvig, G. W. (2011). Chloride regulation of enzyme turnover: application to the role of chloride in photosystem II. Biochemistry, 50(14), 2725-2734. https://doi.org/10.1021/bi2000388
Ponce-García, C. O., Soto-Parra, J. M., Sánchez, E., Muñoz-Márquez, E., Piña-Ramírez, F. J., Flores-Córdova, M. A., ... & Yáñez Muñoz, R. M. (2019). Efficiency of nanoparticle, sulfate, and zinc-chelate use on biomass, yield, and nitrogen assimilation in green beans. Agronomy, 9(3), 128. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy9030128
Pradhan, P., Fischer, G., Van Velthuizen, H., Reusser, D. E., & Kropp, J. P. (2015). Closing yield gaps: how sustainable can we be?. PloS one, 10(6), e0129487. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0129487
Prasad, T. N. V. K. V., Sudhakar, P., Sreenivasulu, Y., Latha, P., Munaswamy, V., Reddy, K. R., Sreeprasad, T.S., Sajanlan, P.S. & Pradeep, T. (2012). Effect of nanoscale zinc oxide particles on the germination, growth and yield of peanut. Journal of plant nutrition, 35(6), 905-927. https://doi.org/10.1080/01904167.2012.663443
Ramírez-Estrada, C. A., Sánchez, E., Flores-Cordova, M. A., Chávez-Mendoza, C., Muñoz-Márquez, E., Palacio-Márquez, A., & Hernández-Figueroa, K. I. (2022). Efficiency and assimilation of nitrogen in bean plants through foliar application of zinc and molybdenum nano fertilizer. Notulae Botanicae Horti Agrobotanici Cluj-Napoca, 50(2), 12719-12719. https://doi.org/10.15835/NBHA50212719
Sánchez, E., Rivero, R. M., Ruiz, J. M., & Romero, L. (2004). Changes in biomass, enzymatic activity and protein concentration in roots and leaves of green bean plants (Phaseolus vulgaris L. cv. Strike) under high NH4NO3 application rates. Scientia horticulturae, 99(3-4), 237-248. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0304-4238(03)00114-6
Schindler, F. V., & Knighton, R. E. (1999). Sample preparation for total nitrogen and 15N‐ratio analysis by the automated Dumas combustion method. Communications in soil science and plant analysis, 30(9-10), 1315-1324. https://doi.org/10.1080/00103629909370287
Silva, M. S. D., Oliveira, G. R. F. D., Merloti, L. F., Bossolani, J. W., Camargos, L. S. D., de Sá, M. E., & Reis, A. R. D. (2020). New insights on molybdenum fertilization in common bean under no-tillage system: rates and application time to obtain high vigor seeds. Journal of Plant Nutrition, 44(10), 1420-1431. https://doi.org/10.1080/01904167.2020.1849290
Singh, M. D. (2017). Nano-fertilizers is a new way to increase nutrients use efficiency in crop production. International Journal of Agriculture Sciences, 9(7), 0975-3710.https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Hari-Meena/publication/344318260_Nanofertilizers_is_a_New_Way_to_Increase_Nutrients_Use_Efficiency_in_Crop_Production/links/5f670700299bf1b53ee440d9/Nano-Fertilizers-is-a-New-Way-to-Increase-Nutrients-Use-Efficiency-in-Crop-Production.pdf
Solanki, M. (2021). The Zn as a vital micronutrient in plants. Journal of microbiology, biotechnology and food sciences, 11(3), e4026-e4026. https://doi.org/10.15414/jmbfs.4026
Subramanian, K. S., Manikandan, A., Thirunavukkarasu, M., & Rahale, C. S. (2015). Nano-fertilizers for balanced crop nutrition. Nanotechnologies in food and agriculture, 69-80. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-14024-7_3
Sun, X., Baldwin, E., & Bai, J. (2019). Applications of gaseous chlorine dioxide on postharvest handling and storage of fruits and vegetables–a review. Food Control, 95, 18-26. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodcont.2018.07.044
Vigani, G., Di Silvestre, D., Agresta, A. M., Donnini, S., Mauri, P., Gehl, C., Bittner, F. & Murgia, I. (2017). Molybdenum and iron mutually impact their homeostasis in cucumber (Cucumis sativus) plants. New Phytologist, 213(3), 1222-1241. https://doi.org/10.1111/nph.14214
Watanabe, K., Fukuzawa, Y., Kawasaki, S. I., Ueno, M., & Kawamitsu, Y. (2016). Effects of potassium chloride and potassium sulfate on sucrose concentration in sugarcane juice under pot conditions. Sugar Tech, 18, 258-265. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12355-015-0392-z
Xu, C., Li, X., & Zhang, L. (2013). The effect of calcium chloride on growth, photosynthesis, and antioxidant responses of Zoysia japonica under drought conditions. PloS One, 8(7), e68214. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0068214
Wellburn, A. R. (1994). The spectral determination of chlorophylls a and b, as well as total carotenoids, using various solvents with spectrophotometers of different resolution. Journal of plant physiology, 144(3), 307-313. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0176-1617(11)81192-2
Wu, G. Q., Feng, R. J., Liang, N., Yuan, H. J., & Sun, W. B. (2015). Sodium chloride stimulates growth and alleviates sorbitol-induced osmotic stress in sugar beet seedlings. Plant growth regulation, 75, 307-316. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10725-014-9954-4
Ybañez, Q. E., Sanchez, P. B., Badayos, R. B., & Agravante, J. U. (2020). Synthesis and characterization of nano zinc oxide foliar fertilizer and its influence on yield and postharvest quality of tomato. e Philippine Agricultural Scientist, 103(1), 55-65.https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Quincy-Ybanez/publication/346658621_Synthesis_and_Characterization_of_Nano_Zinc_Oxide_Foliar_Fertilizer_and_its_Influence_on_Yield_and_Postharvest_Quality_of_Tomato/links/5fd6f3c3299bf140880a6524/Synthesis-and-Characterization-of-Nano-Zinc-Oxide-Foliar-Fertilizer-and-its-Influence-on-Yield-and-Postharvest-Quality-of-Tomato.pdf
Yeboah, S., Asibuo, J., Oteng-Darko, P., Asamoah Adjei, E., Lamptey, M., Owusu Danquah, E., Lamptey, M., Owusu-Danquah, E., Waswa, B. & Butare, L. (2021). Impact of foliar application of zinc and magnesium aminochelate on bean physiology and productivity in Ghana. International Journal of Agronomy, 2021, 1-9. https://doi.org/10.1155/2021/9766709
Yemm, E.W., Cocking, E.C., & Ricketts, R.E. (1955). The determination of amino-acids with ninhydrin. Analyst, 80(948), 209-214. https://doi.org/10.1039/AN9558000209
Zhong, C., Cao, X., Hu, J., Zhu, L., Zhang, J., Huang, J., & Jin, Q. (2017). Nitrogen metabolism in adaptation of photosynthesis to water stress in rice grown under different nitrogen levels. Frontiers in plant science, 8, 1079. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2017.01079

Revista Bio Ciencias por Universidad Autónoma de Nayarit se encuentra bajo una Licencia Creative Commons Atribución-NoComercial-SinDerivadas 4.0 Unported.
Basada en una obra en http://biociencias.uan.edu.mx/.
Permisos que vayan más allá de lo cubierto por esta licencia pueden encontrarse en http://editorial.uan.edu.mx/index.php/BIOCIENCIAS.licencia de Creative Commons Reconocimiento-NoComercial-SinObraDerivada 4.0 Internacional






